
# CycleGAN and pix2pix in PyTorch
This is our ongoing PyTorch implementation for both unpaired and paired image-to-image translation.
The code was written by [Jun-Yan Zhu](https://github.com/junyanz) and [Taesung Park](https://github.com/taesung89).
Check out the original [CycleGAN Torch](https://github.com/junyanz/CycleGAN) and [pix2pix Torch](https://github.com/phillipi/pix2pix) code if you would like to reproduce the exact same results as in the papers.
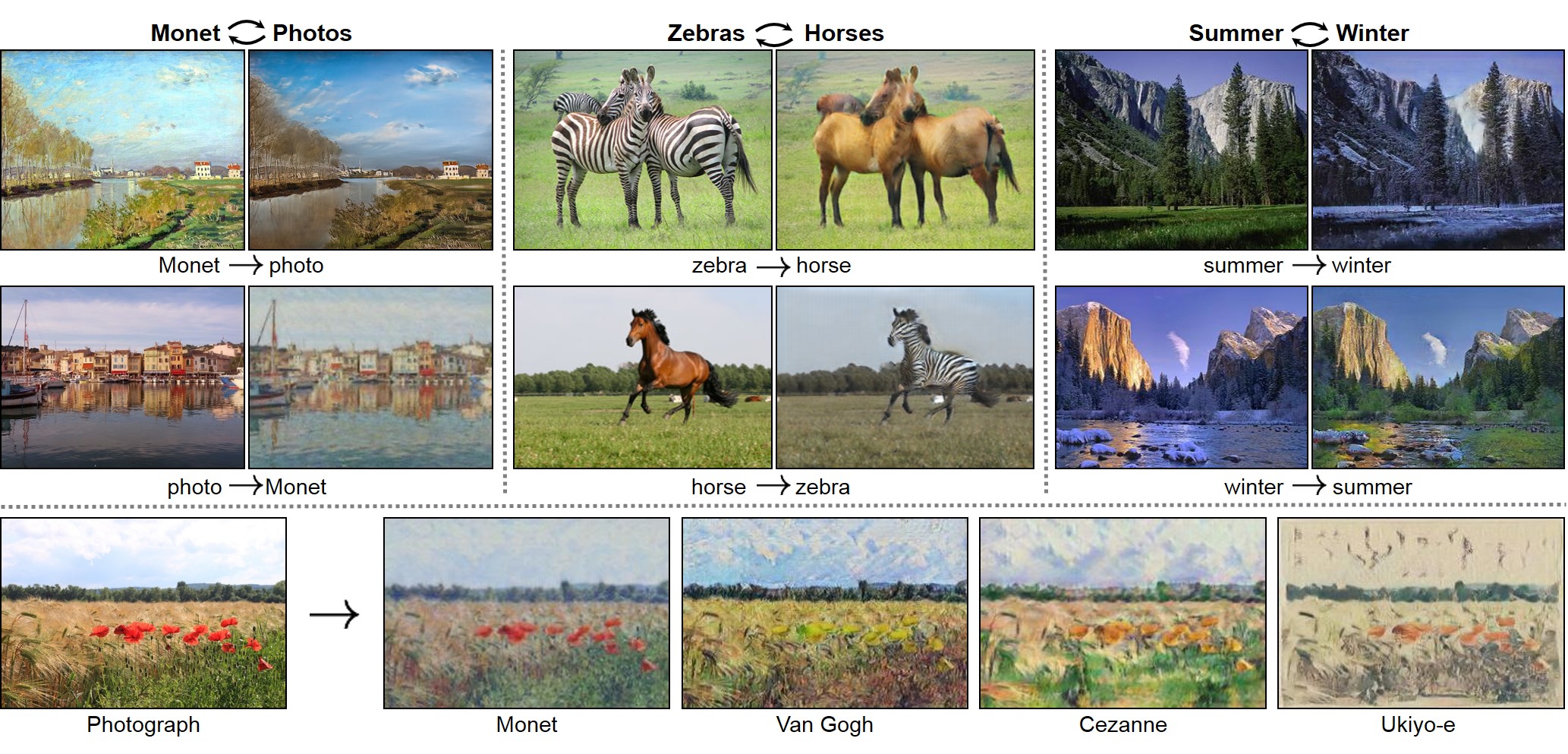
#### CycleGAN: [[Project]](https://junyanz.github.io/CycleGAN/) [[Paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1703.10593.pdf) [[Torch]](https://github.com/junyanz/CycleGAN)
 #### Pix2pix: [[Project]](https://phillipi.github.io/pix2pix/) [[Paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1611.07004v1.pdf) [[Torch]](https://github.com/phillipi/pix2pix)
#### Pix2pix: [[Project]](https://phillipi.github.io/pix2pix/) [[Paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1611.07004v1.pdf) [[Torch]](https://github.com/phillipi/pix2pix)
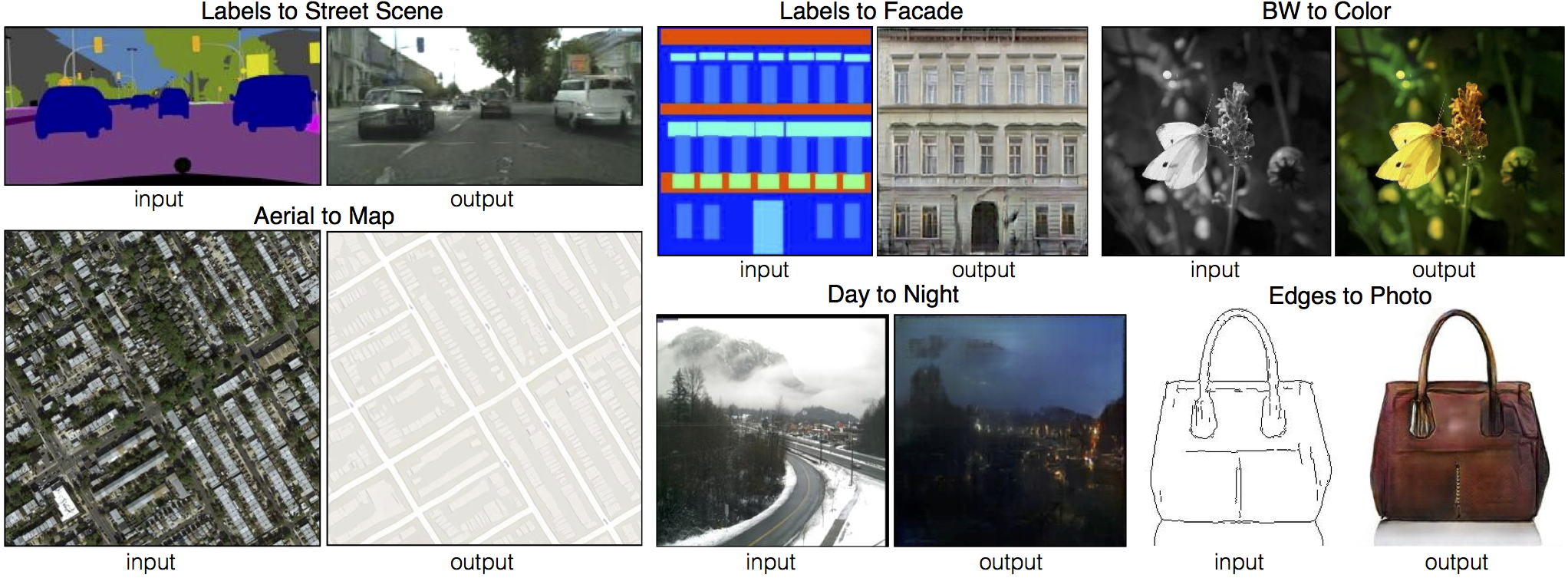 #### [[EdgesCats Demo]](https://affinelayer.com/pixsrv/) [[pix2pix-tensorflow]](https://github.com/affinelayer/pix2pix-tensorflow)
Written by [Christopher Hesse](https://twitter.com/christophrhesse)
#### [[EdgesCats Demo]](https://affinelayer.com/pixsrv/) [[pix2pix-tensorflow]](https://github.com/affinelayer/pix2pix-tensorflow)
Written by [Christopher Hesse](https://twitter.com/christophrhesse)
 If you use this code for your research, please cite:
Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks
[Jun-Yan Zhu](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~junyanz/)\*, [Taesung Park](https://taesung.me/)\*, [Phillip Isola](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~isola/), [Alexei A. Efros](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~efros)
In arxiv, 2017. (* equal contributions)
Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks
[Phillip Isola](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~isola), [Jun-Yan Zhu](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~junyanz), [Tinghui Zhou](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~tinghuiz), [Alexei A. Efros](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~efros)
In CVPR 2017.
## Prerequisites
- Linux or macOS
- Python 2 or 3
- CPU or NVIDIA GPU + CUDA CuDNN
## Getting Started
### Installation
- Install PyTorch and dependencies from http://pytorch.org
- Install Torch vision from the source.
```bash
git clone https://github.com/pytorch/vision
cd vision
python setup.py install
```
- Install python libraries [visdom](https://github.com/facebookresearch/visdom) and [dominate](https://github.com/Knio/dominate).
```bash
pip install visdom
pip install dominate
```
- Clone this repo:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix
cd pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix
```
### CycleGAN train/test
- Download a CycleGAN dataset (e.g. maps):
```bash
bash ./datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh maps
```
- Train a model:
```bash
#!./scripts/train_cyclegan.sh
python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/maps --name maps_cyclegan --model cycle_gan --no_dropout
```
- To view training results and loss plots, run `python -m visdom.server` and click the URL http://localhost:8097. To see more intermediate results, check out `./checkpoints/maps_cyclegan/web/index.html`
- Test the model:
```bash
#!./scripts/test_cyclegan.sh
python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/maps --name maps_cyclegan --model cycle_gan --phase test --no_dropout
```
The test results will be saved to a html file here: `./results/maps_cyclegan/latest_test/index.html`.
### pix2pix train/test
- Download a pix2pix dataset (e.g.facades):
```bash
bash ./datasets/download_pix2pix_dataset.sh facades
```
- Train a model:
```bash
#!./scripts/train_pix2pix.sh
python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --which_model_netG unet_256 --which_direction BtoA --lambda_A 100 --dataset_mode aligned --no_lsgan --norm batch
```
- To view training results and loss plots, run `python -m visdom.server` and click the URL http://localhost:8097. To see more intermediate results, check out `./checkpoints/facades_pix2pix/web/index.html`
- Test the model (`bash ./scripts/test_pix2pix.sh`):
```bash
#!./scripts/test_pix2pix.sh
python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --which_model_netG unet_256 --which_direction BtoA --dataset_mode aligned --norm batch
```
The test results will be saved to a html file here: `./results/facades_pix2pix/latest_val/index.html`.
More example scripts can be found at `scripts` directory.
### Apply a pre-trained model
If you would like to apply a pre-trained model to a collection of input photos (without image pairs), please use `--dataset_mode single` and `--model test` options. Here is a script to apply a pix2pix model to facade label maps (stored in the directory `facades/testB`).
``` bash
#!./scripts/test_single.sh
python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades/testB/ --name facades_pix2pix --model test --which_model_netG unet_256 --which_direction BtoA --dataset_mode single
```
## Training/test Details
- See `options/train_options.py` and `options/base_options.py` for training flags; see `options/test_options.py` and `options/base_options.py` for test flags.
- CPU/GPU (default `--gpu_ids 0`): Set `--gpu_ids -1` to use CPU mode; set `--gpu_ids 0,1,2` for multi-GPU mode. You need a large batch size (e.g. `--batchSize 32`) to benefit from multiple gpus.
- During training, the current results can be viewed using two methods. First, if you set `--display_id` > 0, the results and loss plot will be shown on a local graphics web server launched by [visdom](https://github.com/facebookresearch/visdom). To do this, you should have visdom installed and a server running by the command `python -m visdom.server`. The default server URL is `http://localhost:8097`. `display_id` corresponds to the window ID that is displayed on the `visdom` server. The `visdom` display functionality is turned on by default. To avoid the extra overhead of communicating with `visdom` set `--display_id 0`. Second, the intermediate results are saved to `[opt.checkpoints_dir]/[opt.name]/web/` as an HTML file. To avoid this, set `--no_html`.
- Images can be resized and cropped in different ways using `--resize_or_crop` option. The default option `'resize_and_crop'` resizes the image to be of size `(opt.loadSize, opt.loadSize)` and does a random crop of size `(opt.fineSize, opt.fineSize)`. `'crop'` skips the resizing step and only performs random cropping. `'scale_width'` resizes the image to have width `opt.fineSize` while keeping the aspect ratio. `'scale_width_and_crop'` first resizes the image to have width `opt.loadSize` and then does random cropping of size `(opt.fineSize, opt.fineSize)`.
### CycleGAN Datasets
Download the CycleGAN datasets using the following script. Some of the datasets are collected by other researchers. Please cite their papers if you use the data.
```bash
bash ./datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh dataset_name
```
- `facades`: 400 images from the [CMP Facades dataset](http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/~tylecr1/facade). [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/facades.tex)]
- `cityscapes`: 2975 images from the [Cityscapes training set](https://www.cityscapes-dataset.com). [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/cityscapes.tex)]
- `maps`: 1096 training images scraped from Google Maps.
- `horse2zebra`: 939 horse images and 1177 zebra images downloaded from [ImageNet](http://www.image-net.org) using keywords `wild horse` and `zebra`
- `apple2orange`: 996 apple images and 1020 orange images downloaded from [ImageNet](http://www.image-net.org) using keywords `apple` and `navel orange`.
- `summer2winter_yosemite`: 1273 summer Yosemite images and 854 winter Yosemite images were downloaded using Flickr API. See more details in our paper.
- `monet2photo`, `vangogh2photo`, `ukiyoe2photo`, `cezanne2photo`: The art images were downloaded from [Wikiart](https://www.wikiart.org/). The real photos are downloaded from Flickr using the combination of the tags *landscape* and *landscapephotography*. The training set size of each class is Monet:1074, Cezanne:584, Van Gogh:401, Ukiyo-e:1433, Photographs:6853.
- `iphone2dslr_flower`: both classes of images were downlaoded from Flickr. The training set size of each class is iPhone:1813, DSLR:3316. See more details in our paper.
To train a model on your own datasets, you need to create a data folder with two subdirectories `trainA` and `trainB` that contain images from domain A and B. You can test your model on your training set by setting ``phase='train'`` in `test.lua`. You can also create subdirectories `testA` and `testB` if you have test data.
You should **not** expect our method to work on just any random combination of input and output datasets (e.g. `cats<->keyboards`). From our experiments, we find it works better if two datasets share similar visual content. For example, `landscape painting<->landscape photographs` works much better than `portrait painting <-> landscape photographs`. `zebras<->horses` achieves compelling results while `cats<->dogs` completely fails.
### pix2pix datasets
Download the pix2pix datasets using the following script. Some of the datasets are collected by other researchers. Please cite their papers if you use the data.
```bash
bash ./datasets/download_pix2pix_dataset.sh dataset_name
```
- `facades`: 400 images from [CMP Facades dataset](http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/~tylecr1/facade). [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/facades.tex)]
- `cityscapes`: 2975 images from the [Cityscapes training set](https://www.cityscapes-dataset.com). [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/cityscapes.tex)]
- `maps`: 1096 training images scraped from Google Maps
- `edges2shoes`: 50k training images from [UT Zappos50K dataset](http://vision.cs.utexas.edu/projects/finegrained/utzap50k). Edges are computed by [HED](https://github.com/s9xie/hed) edge detector + post-processing. [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/shoes.tex)]
- `edges2handbags`: 137K Amazon Handbag images from [iGAN project](https://github.com/junyanz/iGAN). Edges are computed by [HED](https://github.com/s9xie/hed) edge detector + post-processing. [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/handbags.tex)]
We provide a python script to generate pix2pix training data in the form of pairs of images {A,B}, where A and B are two different depictions of the same underlying scene. For example, these might be pairs {label map, photo} or {bw image, color image}. Then we can learn to translate A to B or B to A:
Create folder `/path/to/data` with subfolders `A` and `B`. `A` and `B` should each have their own subfolders `train`, `val`, `test`, etc. In `/path/to/data/A/train`, put training images in style A. In `/path/to/data/B/train`, put the corresponding images in style B. Repeat same for other data splits (`val`, `test`, etc).
Corresponding images in a pair {A,B} must be the same size and have the same filename, e.g., `/path/to/data/A/train/1.jpg` is considered to correspond to `/path/to/data/B/train/1.jpg`.
Once the data is formatted this way, call:
```bash
python datasets/combine_A_and_B.py --fold_A /path/to/data/A --fold_B /path/to/data/B --fold_AB /path/to/data
```
This will combine each pair of images (A,B) into a single image file, ready for training.
## Citation
If you use this code for your research, please cite our papers.
```
@article{CycleGAN2017,
title={Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks},
author={Zhu, Jun-Yan and Park, Taesung and Isola, Phillip and Efros, Alexei A},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.10593},
year={2017}
}
@article{pix2pix2016,
title={Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks},
author={Isola, Phillip and Zhu, Jun-Yan and Zhou, Tinghui and Efros, Alexei A},
journal={arxiv},
year={2016}
}
```
## Related Projects
[CycleGAN](https://github.com/junyanz/CycleGAN): Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks
[pix2pix](https://github.com/phillipi/pix2pix): Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial nets
[iGAN](https://github.com/junyanz/iGAN): Interactive Image Generation via Generative Adversarial Networks
## Cat Paper Collection
If you love cats, and love reading cool graphics, vision, and learning papers, please check out the Cat Paper Collection:
[[Github]](https://github.com/junyanz/CatPapers) [[Webpage]](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~junyanz/cat/cat_papers.html)
## Acknowledgments
Code is inspired by [pytorch-DCGAN](https://github.com/pytorch/examples/tree/master/dcgan).
If you use this code for your research, please cite:
Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks
[Jun-Yan Zhu](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~junyanz/)\*, [Taesung Park](https://taesung.me/)\*, [Phillip Isola](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~isola/), [Alexei A. Efros](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~efros)
In arxiv, 2017. (* equal contributions)
Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks
[Phillip Isola](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~isola), [Jun-Yan Zhu](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~junyanz), [Tinghui Zhou](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~tinghuiz), [Alexei A. Efros](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~efros)
In CVPR 2017.
## Prerequisites
- Linux or macOS
- Python 2 or 3
- CPU or NVIDIA GPU + CUDA CuDNN
## Getting Started
### Installation
- Install PyTorch and dependencies from http://pytorch.org
- Install Torch vision from the source.
```bash
git clone https://github.com/pytorch/vision
cd vision
python setup.py install
```
- Install python libraries [visdom](https://github.com/facebookresearch/visdom) and [dominate](https://github.com/Knio/dominate).
```bash
pip install visdom
pip install dominate
```
- Clone this repo:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix
cd pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix
```
### CycleGAN train/test
- Download a CycleGAN dataset (e.g. maps):
```bash
bash ./datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh maps
```
- Train a model:
```bash
#!./scripts/train_cyclegan.sh
python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/maps --name maps_cyclegan --model cycle_gan --no_dropout
```
- To view training results and loss plots, run `python -m visdom.server` and click the URL http://localhost:8097. To see more intermediate results, check out `./checkpoints/maps_cyclegan/web/index.html`
- Test the model:
```bash
#!./scripts/test_cyclegan.sh
python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/maps --name maps_cyclegan --model cycle_gan --phase test --no_dropout
```
The test results will be saved to a html file here: `./results/maps_cyclegan/latest_test/index.html`.
### pix2pix train/test
- Download a pix2pix dataset (e.g.facades):
```bash
bash ./datasets/download_pix2pix_dataset.sh facades
```
- Train a model:
```bash
#!./scripts/train_pix2pix.sh
python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --which_model_netG unet_256 --which_direction BtoA --lambda_A 100 --dataset_mode aligned --no_lsgan --norm batch
```
- To view training results and loss plots, run `python -m visdom.server` and click the URL http://localhost:8097. To see more intermediate results, check out `./checkpoints/facades_pix2pix/web/index.html`
- Test the model (`bash ./scripts/test_pix2pix.sh`):
```bash
#!./scripts/test_pix2pix.sh
python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --which_model_netG unet_256 --which_direction BtoA --dataset_mode aligned --norm batch
```
The test results will be saved to a html file here: `./results/facades_pix2pix/latest_val/index.html`.
More example scripts can be found at `scripts` directory.
### Apply a pre-trained model
If you would like to apply a pre-trained model to a collection of input photos (without image pairs), please use `--dataset_mode single` and `--model test` options. Here is a script to apply a pix2pix model to facade label maps (stored in the directory `facades/testB`).
``` bash
#!./scripts/test_single.sh
python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades/testB/ --name facades_pix2pix --model test --which_model_netG unet_256 --which_direction BtoA --dataset_mode single
```
## Training/test Details
- See `options/train_options.py` and `options/base_options.py` for training flags; see `options/test_options.py` and `options/base_options.py` for test flags.
- CPU/GPU (default `--gpu_ids 0`): Set `--gpu_ids -1` to use CPU mode; set `--gpu_ids 0,1,2` for multi-GPU mode. You need a large batch size (e.g. `--batchSize 32`) to benefit from multiple gpus.
- During training, the current results can be viewed using two methods. First, if you set `--display_id` > 0, the results and loss plot will be shown on a local graphics web server launched by [visdom](https://github.com/facebookresearch/visdom). To do this, you should have visdom installed and a server running by the command `python -m visdom.server`. The default server URL is `http://localhost:8097`. `display_id` corresponds to the window ID that is displayed on the `visdom` server. The `visdom` display functionality is turned on by default. To avoid the extra overhead of communicating with `visdom` set `--display_id 0`. Second, the intermediate results are saved to `[opt.checkpoints_dir]/[opt.name]/web/` as an HTML file. To avoid this, set `--no_html`.
- Images can be resized and cropped in different ways using `--resize_or_crop` option. The default option `'resize_and_crop'` resizes the image to be of size `(opt.loadSize, opt.loadSize)` and does a random crop of size `(opt.fineSize, opt.fineSize)`. `'crop'` skips the resizing step and only performs random cropping. `'scale_width'` resizes the image to have width `opt.fineSize` while keeping the aspect ratio. `'scale_width_and_crop'` first resizes the image to have width `opt.loadSize` and then does random cropping of size `(opt.fineSize, opt.fineSize)`.
### CycleGAN Datasets
Download the CycleGAN datasets using the following script. Some of the datasets are collected by other researchers. Please cite their papers if you use the data.
```bash
bash ./datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh dataset_name
```
- `facades`: 400 images from the [CMP Facades dataset](http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/~tylecr1/facade). [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/facades.tex)]
- `cityscapes`: 2975 images from the [Cityscapes training set](https://www.cityscapes-dataset.com). [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/cityscapes.tex)]
- `maps`: 1096 training images scraped from Google Maps.
- `horse2zebra`: 939 horse images and 1177 zebra images downloaded from [ImageNet](http://www.image-net.org) using keywords `wild horse` and `zebra`
- `apple2orange`: 996 apple images and 1020 orange images downloaded from [ImageNet](http://www.image-net.org) using keywords `apple` and `navel orange`.
- `summer2winter_yosemite`: 1273 summer Yosemite images and 854 winter Yosemite images were downloaded using Flickr API. See more details in our paper.
- `monet2photo`, `vangogh2photo`, `ukiyoe2photo`, `cezanne2photo`: The art images were downloaded from [Wikiart](https://www.wikiart.org/). The real photos are downloaded from Flickr using the combination of the tags *landscape* and *landscapephotography*. The training set size of each class is Monet:1074, Cezanne:584, Van Gogh:401, Ukiyo-e:1433, Photographs:6853.
- `iphone2dslr_flower`: both classes of images were downlaoded from Flickr. The training set size of each class is iPhone:1813, DSLR:3316. See more details in our paper.
To train a model on your own datasets, you need to create a data folder with two subdirectories `trainA` and `trainB` that contain images from domain A and B. You can test your model on your training set by setting ``phase='train'`` in `test.lua`. You can also create subdirectories `testA` and `testB` if you have test data.
You should **not** expect our method to work on just any random combination of input and output datasets (e.g. `cats<->keyboards`). From our experiments, we find it works better if two datasets share similar visual content. For example, `landscape painting<->landscape photographs` works much better than `portrait painting <-> landscape photographs`. `zebras<->horses` achieves compelling results while `cats<->dogs` completely fails.
### pix2pix datasets
Download the pix2pix datasets using the following script. Some of the datasets are collected by other researchers. Please cite their papers if you use the data.
```bash
bash ./datasets/download_pix2pix_dataset.sh dataset_name
```
- `facades`: 400 images from [CMP Facades dataset](http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/~tylecr1/facade). [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/facades.tex)]
- `cityscapes`: 2975 images from the [Cityscapes training set](https://www.cityscapes-dataset.com). [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/cityscapes.tex)]
- `maps`: 1096 training images scraped from Google Maps
- `edges2shoes`: 50k training images from [UT Zappos50K dataset](http://vision.cs.utexas.edu/projects/finegrained/utzap50k). Edges are computed by [HED](https://github.com/s9xie/hed) edge detector + post-processing. [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/shoes.tex)]
- `edges2handbags`: 137K Amazon Handbag images from [iGAN project](https://github.com/junyanz/iGAN). Edges are computed by [HED](https://github.com/s9xie/hed) edge detector + post-processing. [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/handbags.tex)]
We provide a python script to generate pix2pix training data in the form of pairs of images {A,B}, where A and B are two different depictions of the same underlying scene. For example, these might be pairs {label map, photo} or {bw image, color image}. Then we can learn to translate A to B or B to A:
Create folder `/path/to/data` with subfolders `A` and `B`. `A` and `B` should each have their own subfolders `train`, `val`, `test`, etc. In `/path/to/data/A/train`, put training images in style A. In `/path/to/data/B/train`, put the corresponding images in style B. Repeat same for other data splits (`val`, `test`, etc).
Corresponding images in a pair {A,B} must be the same size and have the same filename, e.g., `/path/to/data/A/train/1.jpg` is considered to correspond to `/path/to/data/B/train/1.jpg`.
Once the data is formatted this way, call:
```bash
python datasets/combine_A_and_B.py --fold_A /path/to/data/A --fold_B /path/to/data/B --fold_AB /path/to/data
```
This will combine each pair of images (A,B) into a single image file, ready for training.
## Citation
If you use this code for your research, please cite our papers.
```
@article{CycleGAN2017,
title={Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks},
author={Zhu, Jun-Yan and Park, Taesung and Isola, Phillip and Efros, Alexei A},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.10593},
year={2017}
}
@article{pix2pix2016,
title={Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks},
author={Isola, Phillip and Zhu, Jun-Yan and Zhou, Tinghui and Efros, Alexei A},
journal={arxiv},
year={2016}
}
```
## Related Projects
[CycleGAN](https://github.com/junyanz/CycleGAN): Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks
[pix2pix](https://github.com/phillipi/pix2pix): Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial nets
[iGAN](https://github.com/junyanz/iGAN): Interactive Image Generation via Generative Adversarial Networks
## Cat Paper Collection
If you love cats, and love reading cool graphics, vision, and learning papers, please check out the Cat Paper Collection:
[[Github]](https://github.com/junyanz/CatPapers) [[Webpage]](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~junyanz/cat/cat_papers.html)
## Acknowledgments
Code is inspired by [pytorch-DCGAN](https://github.com/pytorch/examples/tree/master/dcgan).

 #### Pix2pix: [[Project]](https://phillipi.github.io/pix2pix/) [[Paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1611.07004v1.pdf) [[Torch]](https://github.com/phillipi/pix2pix)
#### Pix2pix: [[Project]](https://phillipi.github.io/pix2pix/) [[Paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1611.07004v1.pdf) [[Torch]](https://github.com/phillipi/pix2pix)
 #### [[EdgesCats Demo]](https://affinelayer.com/pixsrv/) [[pix2pix-tensorflow]](https://github.com/affinelayer/pix2pix-tensorflow)
Written by [Christopher Hesse](https://twitter.com/christophrhesse)
#### [[EdgesCats Demo]](https://affinelayer.com/pixsrv/) [[pix2pix-tensorflow]](https://github.com/affinelayer/pix2pix-tensorflow)
Written by [Christopher Hesse](https://twitter.com/christophrhesse)
 If you use this code for your research, please cite:
Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks
[Jun-Yan Zhu](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~junyanz/)\*, [Taesung Park](https://taesung.me/)\*, [Phillip Isola](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~isola/), [Alexei A. Efros](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~efros)
In arxiv, 2017. (* equal contributions)
Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks
[Phillip Isola](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~isola), [Jun-Yan Zhu](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~junyanz), [Tinghui Zhou](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~tinghuiz), [Alexei A. Efros](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~efros)
In CVPR 2017.
## Prerequisites
- Linux or macOS
- Python 2 or 3
- CPU or NVIDIA GPU + CUDA CuDNN
## Getting Started
### Installation
- Install PyTorch and dependencies from http://pytorch.org
- Install Torch vision from the source.
```bash
git clone https://github.com/pytorch/vision
cd vision
python setup.py install
```
- Install python libraries [visdom](https://github.com/facebookresearch/visdom) and [dominate](https://github.com/Knio/dominate).
```bash
pip install visdom
pip install dominate
```
- Clone this repo:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix
cd pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix
```
### CycleGAN train/test
- Download a CycleGAN dataset (e.g. maps):
```bash
bash ./datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh maps
```
- Train a model:
```bash
#!./scripts/train_cyclegan.sh
python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/maps --name maps_cyclegan --model cycle_gan --no_dropout
```
- To view training results and loss plots, run `python -m visdom.server` and click the URL http://localhost:8097. To see more intermediate results, check out `./checkpoints/maps_cyclegan/web/index.html`
- Test the model:
```bash
#!./scripts/test_cyclegan.sh
python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/maps --name maps_cyclegan --model cycle_gan --phase test --no_dropout
```
The test results will be saved to a html file here: `./results/maps_cyclegan/latest_test/index.html`.
### pix2pix train/test
- Download a pix2pix dataset (e.g.facades):
```bash
bash ./datasets/download_pix2pix_dataset.sh facades
```
- Train a model:
```bash
#!./scripts/train_pix2pix.sh
python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --which_model_netG unet_256 --which_direction BtoA --lambda_A 100 --dataset_mode aligned --no_lsgan --norm batch
```
- To view training results and loss plots, run `python -m visdom.server` and click the URL http://localhost:8097. To see more intermediate results, check out `./checkpoints/facades_pix2pix/web/index.html`
- Test the model (`bash ./scripts/test_pix2pix.sh`):
```bash
#!./scripts/test_pix2pix.sh
python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --which_model_netG unet_256 --which_direction BtoA --dataset_mode aligned --norm batch
```
The test results will be saved to a html file here: `./results/facades_pix2pix/latest_val/index.html`.
More example scripts can be found at `scripts` directory.
### Apply a pre-trained model
If you would like to apply a pre-trained model to a collection of input photos (without image pairs), please use `--dataset_mode single` and `--model test` options. Here is a script to apply a pix2pix model to facade label maps (stored in the directory `facades/testB`).
``` bash
#!./scripts/test_single.sh
python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades/testB/ --name facades_pix2pix --model test --which_model_netG unet_256 --which_direction BtoA --dataset_mode single
```
## Training/test Details
- See `options/train_options.py` and `options/base_options.py` for training flags; see `options/test_options.py` and `options/base_options.py` for test flags.
- CPU/GPU (default `--gpu_ids 0`): Set `--gpu_ids -1` to use CPU mode; set `--gpu_ids 0,1,2` for multi-GPU mode. You need a large batch size (e.g. `--batchSize 32`) to benefit from multiple gpus.
- During training, the current results can be viewed using two methods. First, if you set `--display_id` > 0, the results and loss plot will be shown on a local graphics web server launched by [visdom](https://github.com/facebookresearch/visdom). To do this, you should have visdom installed and a server running by the command `python -m visdom.server`. The default server URL is `http://localhost:8097`. `display_id` corresponds to the window ID that is displayed on the `visdom` server. The `visdom` display functionality is turned on by default. To avoid the extra overhead of communicating with `visdom` set `--display_id 0`. Second, the intermediate results are saved to `[opt.checkpoints_dir]/[opt.name]/web/` as an HTML file. To avoid this, set `--no_html`.
- Images can be resized and cropped in different ways using `--resize_or_crop` option. The default option `'resize_and_crop'` resizes the image to be of size `(opt.loadSize, opt.loadSize)` and does a random crop of size `(opt.fineSize, opt.fineSize)`. `'crop'` skips the resizing step and only performs random cropping. `'scale_width'` resizes the image to have width `opt.fineSize` while keeping the aspect ratio. `'scale_width_and_crop'` first resizes the image to have width `opt.loadSize` and then does random cropping of size `(opt.fineSize, opt.fineSize)`.
### CycleGAN Datasets
Download the CycleGAN datasets using the following script. Some of the datasets are collected by other researchers. Please cite their papers if you use the data.
```bash
bash ./datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh dataset_name
```
- `facades`: 400 images from the [CMP Facades dataset](http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/~tylecr1/facade). [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/facades.tex)]
- `cityscapes`: 2975 images from the [Cityscapes training set](https://www.cityscapes-dataset.com). [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/cityscapes.tex)]
- `maps`: 1096 training images scraped from Google Maps.
- `horse2zebra`: 939 horse images and 1177 zebra images downloaded from [ImageNet](http://www.image-net.org) using keywords `wild horse` and `zebra`
- `apple2orange`: 996 apple images and 1020 orange images downloaded from [ImageNet](http://www.image-net.org) using keywords `apple` and `navel orange`.
- `summer2winter_yosemite`: 1273 summer Yosemite images and 854 winter Yosemite images were downloaded using Flickr API. See more details in our paper.
- `monet2photo`, `vangogh2photo`, `ukiyoe2photo`, `cezanne2photo`: The art images were downloaded from [Wikiart](https://www.wikiart.org/). The real photos are downloaded from Flickr using the combination of the tags *landscape* and *landscapephotography*. The training set size of each class is Monet:1074, Cezanne:584, Van Gogh:401, Ukiyo-e:1433, Photographs:6853.
- `iphone2dslr_flower`: both classes of images were downlaoded from Flickr. The training set size of each class is iPhone:1813, DSLR:3316. See more details in our paper.
To train a model on your own datasets, you need to create a data folder with two subdirectories `trainA` and `trainB` that contain images from domain A and B. You can test your model on your training set by setting ``phase='train'`` in `test.lua`. You can also create subdirectories `testA` and `testB` if you have test data.
You should **not** expect our method to work on just any random combination of input and output datasets (e.g. `cats<->keyboards`). From our experiments, we find it works better if two datasets share similar visual content. For example, `landscape painting<->landscape photographs` works much better than `portrait painting <-> landscape photographs`. `zebras<->horses` achieves compelling results while `cats<->dogs` completely fails.
### pix2pix datasets
Download the pix2pix datasets using the following script. Some of the datasets are collected by other researchers. Please cite their papers if you use the data.
```bash
bash ./datasets/download_pix2pix_dataset.sh dataset_name
```
- `facades`: 400 images from [CMP Facades dataset](http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/~tylecr1/facade). [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/facades.tex)]
- `cityscapes`: 2975 images from the [Cityscapes training set](https://www.cityscapes-dataset.com). [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/cityscapes.tex)]
- `maps`: 1096 training images scraped from Google Maps
- `edges2shoes`: 50k training images from [UT Zappos50K dataset](http://vision.cs.utexas.edu/projects/finegrained/utzap50k). Edges are computed by [HED](https://github.com/s9xie/hed) edge detector + post-processing. [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/shoes.tex)]
- `edges2handbags`: 137K Amazon Handbag images from [iGAN project](https://github.com/junyanz/iGAN). Edges are computed by [HED](https://github.com/s9xie/hed) edge detector + post-processing. [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/handbags.tex)]
We provide a python script to generate pix2pix training data in the form of pairs of images {A,B}, where A and B are two different depictions of the same underlying scene. For example, these might be pairs {label map, photo} or {bw image, color image}. Then we can learn to translate A to B or B to A:
Create folder `/path/to/data` with subfolders `A` and `B`. `A` and `B` should each have their own subfolders `train`, `val`, `test`, etc. In `/path/to/data/A/train`, put training images in style A. In `/path/to/data/B/train`, put the corresponding images in style B. Repeat same for other data splits (`val`, `test`, etc).
Corresponding images in a pair {A,B} must be the same size and have the same filename, e.g., `/path/to/data/A/train/1.jpg` is considered to correspond to `/path/to/data/B/train/1.jpg`.
Once the data is formatted this way, call:
```bash
python datasets/combine_A_and_B.py --fold_A /path/to/data/A --fold_B /path/to/data/B --fold_AB /path/to/data
```
This will combine each pair of images (A,B) into a single image file, ready for training.
## Citation
If you use this code for your research, please cite our papers.
```
@article{CycleGAN2017,
title={Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks},
author={Zhu, Jun-Yan and Park, Taesung and Isola, Phillip and Efros, Alexei A},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.10593},
year={2017}
}
@article{pix2pix2016,
title={Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks},
author={Isola, Phillip and Zhu, Jun-Yan and Zhou, Tinghui and Efros, Alexei A},
journal={arxiv},
year={2016}
}
```
## Related Projects
[CycleGAN](https://github.com/junyanz/CycleGAN): Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks
[pix2pix](https://github.com/phillipi/pix2pix): Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial nets
[iGAN](https://github.com/junyanz/iGAN): Interactive Image Generation via Generative Adversarial Networks
## Cat Paper Collection
If you love cats, and love reading cool graphics, vision, and learning papers, please check out the Cat Paper Collection:
[[Github]](https://github.com/junyanz/CatPapers) [[Webpage]](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~junyanz/cat/cat_papers.html)
## Acknowledgments
Code is inspired by [pytorch-DCGAN](https://github.com/pytorch/examples/tree/master/dcgan).
If you use this code for your research, please cite:
Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks
[Jun-Yan Zhu](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~junyanz/)\*, [Taesung Park](https://taesung.me/)\*, [Phillip Isola](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~isola/), [Alexei A. Efros](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~efros)
In arxiv, 2017. (* equal contributions)
Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks
[Phillip Isola](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~isola), [Jun-Yan Zhu](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~junyanz), [Tinghui Zhou](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~tinghuiz), [Alexei A. Efros](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~efros)
In CVPR 2017.
## Prerequisites
- Linux or macOS
- Python 2 or 3
- CPU or NVIDIA GPU + CUDA CuDNN
## Getting Started
### Installation
- Install PyTorch and dependencies from http://pytorch.org
- Install Torch vision from the source.
```bash
git clone https://github.com/pytorch/vision
cd vision
python setup.py install
```
- Install python libraries [visdom](https://github.com/facebookresearch/visdom) and [dominate](https://github.com/Knio/dominate).
```bash
pip install visdom
pip install dominate
```
- Clone this repo:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix
cd pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix
```
### CycleGAN train/test
- Download a CycleGAN dataset (e.g. maps):
```bash
bash ./datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh maps
```
- Train a model:
```bash
#!./scripts/train_cyclegan.sh
python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/maps --name maps_cyclegan --model cycle_gan --no_dropout
```
- To view training results and loss plots, run `python -m visdom.server` and click the URL http://localhost:8097. To see more intermediate results, check out `./checkpoints/maps_cyclegan/web/index.html`
- Test the model:
```bash
#!./scripts/test_cyclegan.sh
python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/maps --name maps_cyclegan --model cycle_gan --phase test --no_dropout
```
The test results will be saved to a html file here: `./results/maps_cyclegan/latest_test/index.html`.
### pix2pix train/test
- Download a pix2pix dataset (e.g.facades):
```bash
bash ./datasets/download_pix2pix_dataset.sh facades
```
- Train a model:
```bash
#!./scripts/train_pix2pix.sh
python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --which_model_netG unet_256 --which_direction BtoA --lambda_A 100 --dataset_mode aligned --no_lsgan --norm batch
```
- To view training results and loss plots, run `python -m visdom.server` and click the URL http://localhost:8097. To see more intermediate results, check out `./checkpoints/facades_pix2pix/web/index.html`
- Test the model (`bash ./scripts/test_pix2pix.sh`):
```bash
#!./scripts/test_pix2pix.sh
python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --which_model_netG unet_256 --which_direction BtoA --dataset_mode aligned --norm batch
```
The test results will be saved to a html file here: `./results/facades_pix2pix/latest_val/index.html`.
More example scripts can be found at `scripts` directory.
### Apply a pre-trained model
If you would like to apply a pre-trained model to a collection of input photos (without image pairs), please use `--dataset_mode single` and `--model test` options. Here is a script to apply a pix2pix model to facade label maps (stored in the directory `facades/testB`).
``` bash
#!./scripts/test_single.sh
python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades/testB/ --name facades_pix2pix --model test --which_model_netG unet_256 --which_direction BtoA --dataset_mode single
```
## Training/test Details
- See `options/train_options.py` and `options/base_options.py` for training flags; see `options/test_options.py` and `options/base_options.py` for test flags.
- CPU/GPU (default `--gpu_ids 0`): Set `--gpu_ids -1` to use CPU mode; set `--gpu_ids 0,1,2` for multi-GPU mode. You need a large batch size (e.g. `--batchSize 32`) to benefit from multiple gpus.
- During training, the current results can be viewed using two methods. First, if you set `--display_id` > 0, the results and loss plot will be shown on a local graphics web server launched by [visdom](https://github.com/facebookresearch/visdom). To do this, you should have visdom installed and a server running by the command `python -m visdom.server`. The default server URL is `http://localhost:8097`. `display_id` corresponds to the window ID that is displayed on the `visdom` server. The `visdom` display functionality is turned on by default. To avoid the extra overhead of communicating with `visdom` set `--display_id 0`. Second, the intermediate results are saved to `[opt.checkpoints_dir]/[opt.name]/web/` as an HTML file. To avoid this, set `--no_html`.
- Images can be resized and cropped in different ways using `--resize_or_crop` option. The default option `'resize_and_crop'` resizes the image to be of size `(opt.loadSize, opt.loadSize)` and does a random crop of size `(opt.fineSize, opt.fineSize)`. `'crop'` skips the resizing step and only performs random cropping. `'scale_width'` resizes the image to have width `opt.fineSize` while keeping the aspect ratio. `'scale_width_and_crop'` first resizes the image to have width `opt.loadSize` and then does random cropping of size `(opt.fineSize, opt.fineSize)`.
### CycleGAN Datasets
Download the CycleGAN datasets using the following script. Some of the datasets are collected by other researchers. Please cite their papers if you use the data.
```bash
bash ./datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh dataset_name
```
- `facades`: 400 images from the [CMP Facades dataset](http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/~tylecr1/facade). [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/facades.tex)]
- `cityscapes`: 2975 images from the [Cityscapes training set](https://www.cityscapes-dataset.com). [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/cityscapes.tex)]
- `maps`: 1096 training images scraped from Google Maps.
- `horse2zebra`: 939 horse images and 1177 zebra images downloaded from [ImageNet](http://www.image-net.org) using keywords `wild horse` and `zebra`
- `apple2orange`: 996 apple images and 1020 orange images downloaded from [ImageNet](http://www.image-net.org) using keywords `apple` and `navel orange`.
- `summer2winter_yosemite`: 1273 summer Yosemite images and 854 winter Yosemite images were downloaded using Flickr API. See more details in our paper.
- `monet2photo`, `vangogh2photo`, `ukiyoe2photo`, `cezanne2photo`: The art images were downloaded from [Wikiart](https://www.wikiart.org/). The real photos are downloaded from Flickr using the combination of the tags *landscape* and *landscapephotography*. The training set size of each class is Monet:1074, Cezanne:584, Van Gogh:401, Ukiyo-e:1433, Photographs:6853.
- `iphone2dslr_flower`: both classes of images were downlaoded from Flickr. The training set size of each class is iPhone:1813, DSLR:3316. See more details in our paper.
To train a model on your own datasets, you need to create a data folder with two subdirectories `trainA` and `trainB` that contain images from domain A and B. You can test your model on your training set by setting ``phase='train'`` in `test.lua`. You can also create subdirectories `testA` and `testB` if you have test data.
You should **not** expect our method to work on just any random combination of input and output datasets (e.g. `cats<->keyboards`). From our experiments, we find it works better if two datasets share similar visual content. For example, `landscape painting<->landscape photographs` works much better than `portrait painting <-> landscape photographs`. `zebras<->horses` achieves compelling results while `cats<->dogs` completely fails.
### pix2pix datasets
Download the pix2pix datasets using the following script. Some of the datasets are collected by other researchers. Please cite their papers if you use the data.
```bash
bash ./datasets/download_pix2pix_dataset.sh dataset_name
```
- `facades`: 400 images from [CMP Facades dataset](http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/~tylecr1/facade). [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/facades.tex)]
- `cityscapes`: 2975 images from the [Cityscapes training set](https://www.cityscapes-dataset.com). [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/cityscapes.tex)]
- `maps`: 1096 training images scraped from Google Maps
- `edges2shoes`: 50k training images from [UT Zappos50K dataset](http://vision.cs.utexas.edu/projects/finegrained/utzap50k). Edges are computed by [HED](https://github.com/s9xie/hed) edge detector + post-processing. [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/shoes.tex)]
- `edges2handbags`: 137K Amazon Handbag images from [iGAN project](https://github.com/junyanz/iGAN). Edges are computed by [HED](https://github.com/s9xie/hed) edge detector + post-processing. [[Citation](datasets/bibtex/handbags.tex)]
We provide a python script to generate pix2pix training data in the form of pairs of images {A,B}, where A and B are two different depictions of the same underlying scene. For example, these might be pairs {label map, photo} or {bw image, color image}. Then we can learn to translate A to B or B to A:
Create folder `/path/to/data` with subfolders `A` and `B`. `A` and `B` should each have their own subfolders `train`, `val`, `test`, etc. In `/path/to/data/A/train`, put training images in style A. In `/path/to/data/B/train`, put the corresponding images in style B. Repeat same for other data splits (`val`, `test`, etc).
Corresponding images in a pair {A,B} must be the same size and have the same filename, e.g., `/path/to/data/A/train/1.jpg` is considered to correspond to `/path/to/data/B/train/1.jpg`.
Once the data is formatted this way, call:
```bash
python datasets/combine_A_and_B.py --fold_A /path/to/data/A --fold_B /path/to/data/B --fold_AB /path/to/data
```
This will combine each pair of images (A,B) into a single image file, ready for training.
## Citation
If you use this code for your research, please cite our papers.
```
@article{CycleGAN2017,
title={Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks},
author={Zhu, Jun-Yan and Park, Taesung and Isola, Phillip and Efros, Alexei A},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.10593},
year={2017}
}
@article{pix2pix2016,
title={Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks},
author={Isola, Phillip and Zhu, Jun-Yan and Zhou, Tinghui and Efros, Alexei A},
journal={arxiv},
year={2016}
}
```
## Related Projects
[CycleGAN](https://github.com/junyanz/CycleGAN): Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks
[pix2pix](https://github.com/phillipi/pix2pix): Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial nets
[iGAN](https://github.com/junyanz/iGAN): Interactive Image Generation via Generative Adversarial Networks
## Cat Paper Collection
If you love cats, and love reading cool graphics, vision, and learning papers, please check out the Cat Paper Collection:
[[Github]](https://github.com/junyanz/CatPapers) [[Webpage]](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~junyanz/cat/cat_papers.html)
## Acknowledgments
Code is inspired by [pytorch-DCGAN](https://github.com/pytorch/examples/tree/master/dcgan).